Online Reports & Tools
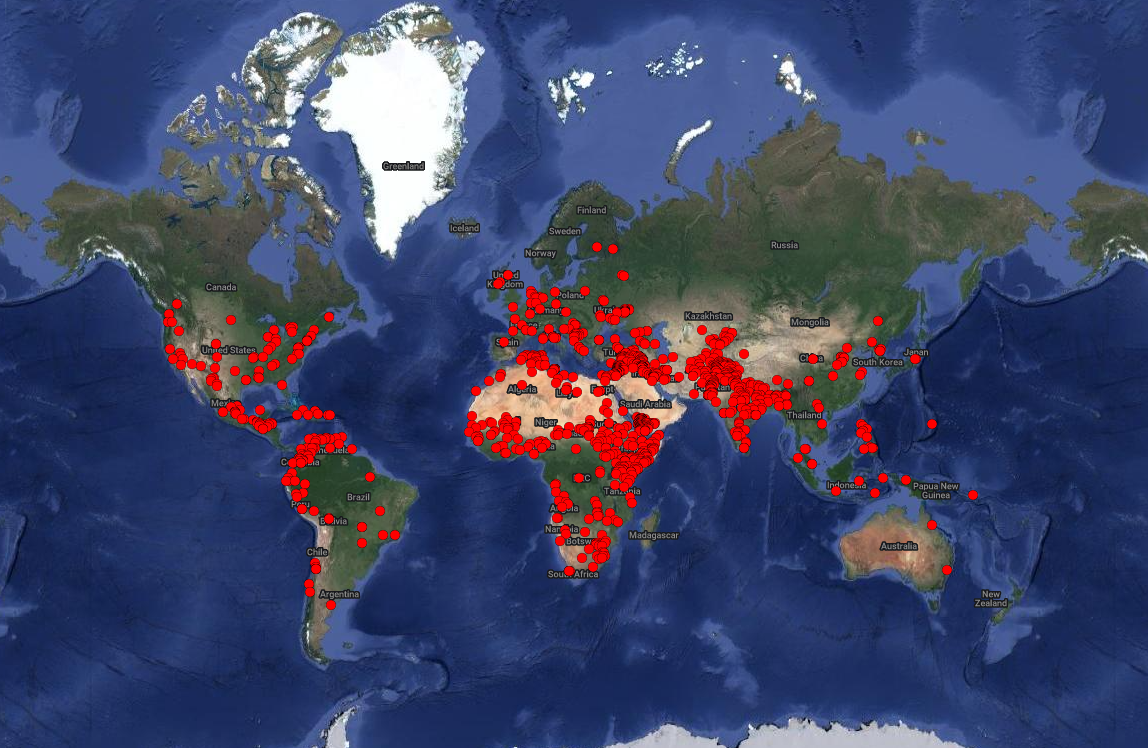
SCIENCE-BASED OPEN-SOURCE RESEARCH PUBLICATIONS ACTIVELY INFORMING WATER POLICIES AND INVESTMENTS
Global Media Impressions
PEOPLE POTENTIALLY REACHED ANNUALLY BY MEDIA COVERAGE ON WATER CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS
Stakeholders Engaged
CROSS-SECTOR STAKEHOLDERS CONVENED TO ADVANCE WATER RESILIENCE SPANNING UTILITIES, POLICYMAKERS, COMPANIES & NGOS
What We Do
The Pacific Institute envisions a world in which society, the economy, and the environment have the water they need to thrive now and in the future. Our 2030 goal is to catalyze the transformation to water resilience in the face of climate change.



Why We Do It
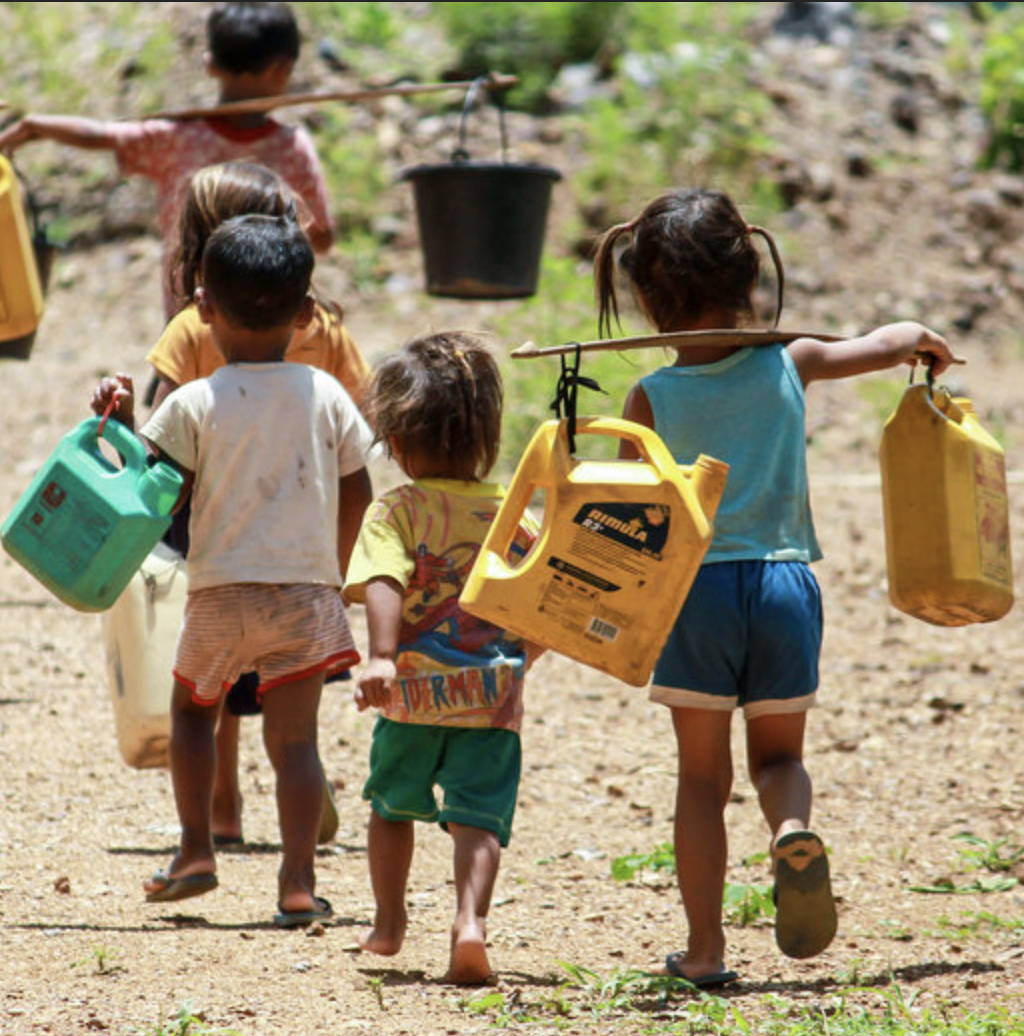
MORE THAN 2.2 BILLION PEOPLE GLOBALLY LACK ACCESS TO SAFELY MANAGED DRINKING WATER.1
WATER-RELATED DISASTERS REPRESENT 90 PERCENT OF ALL NATURAL DISASTERS ON EARTH.2
Annual investment of $1 trillion is needed globally to sustainably manage water by 2030.3
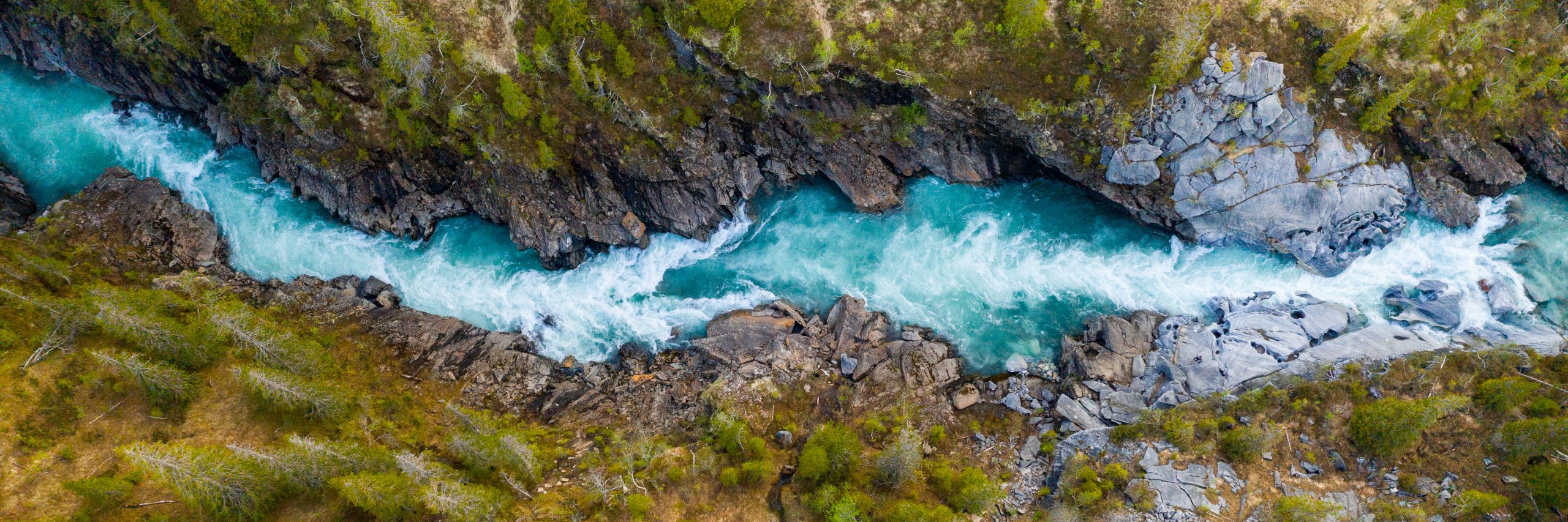
The need has never been greater. For 35 years, we have provided trusted science-based research, recommended feasible policy and practice solutions, and convened diverse stakeholders —from frontline communities and water utilities to Fortune 500 companies and governments —to advance solutions for the world’s most urgent water challenges. From the Colorado River Basin of the drought-prone US West to the world stage at the UN Climate Change Conference in Egypt, decision-makers turn to the Pacific Institute for science-backed leadership on water resilience now more than ever.
1UN Water, 2021; 2UN Water, n.d.; 3WRI, 2020
THE LATEST

ANNOUNCEMENTS
March 2024 NewsletterCollaboration is core to the Pacific Institute’s approach. We build cross-sector alliances to tackle complex water challenges.
You Can Help
The Pacific Institute’s work is fueled by financial support from people like you. Together, we are building the evidence base through science-based research, informing communities and decision makers about solutions, and influencing policies. Join us in this effort to build water resilience—and help solve the world’s water challenges.
Connect With Us
Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest news, publications, resources, and more.
By submitting this form, you are consenting to receive marketing emails from: . You can revoke your consent to receive emails at any time by using the SafeUnsubscribe® link, found at the bottom of every email. Emails are serviced by Constant Contact